What is Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD)?
Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD) is a progressive neurological condition. It presents complex challenges, not only to people living with a CBD diagnosis but also to their families, caregivers, and the healthcare professionals who support them.
CBD disease involves the degeneration of brain cells caused by the accumulation of abnormal tau proteins in the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia. This leads to a range of symptoms affecting movement, which usually begins on one side of the body, as well as affecting cognition. CBD may also affect speech, memory, and behaviour.
You may have also heard the term “CBS”, which stands for Corticobasal Syndrome. Although CBD and CBS are often used interchangeably, they do mean different things, which can get confusing. CBD is a pathology, the thing that is causing the disease in the brain. CBS is a syndrome which is a collection of symptoms. CBD in the brain can show as different diseases in life, but most people diagnosed with CBS have CBD causing it, which is why they are used interchangeably. You can read more about their distinction in our CBD Vs CBS blog.
The purpose of this page is to educate anyone looking for information about CBD, to help improve understanding of the condition and the care and support available.
WANT TO KNOW MORE ABOUT CBD?
Download our PDF for a more in depth introduction to PSP & CBD.
PREVALENCE AND CAUSES OF CBD IN THE UK
Corticobasal Degeneration – often abbreviated to CBD – is a rare but complex neurological disorder that has a notable impact within the UK.
Prevalence of CBD
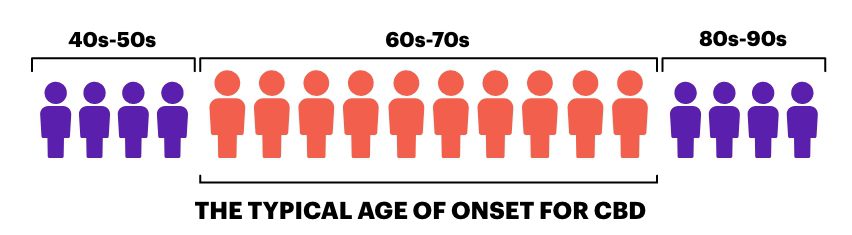
CBD is considered a rare disease, affecting approximately 5 individuals per 100,000 population. This prevalence rate places it on par with conditions like Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) and Motor Neuron Disease (MND), but it remains significantly less common than Parkinson’s disease. The typical age of onset for CBD is between 60 and 70 years, though cases have been documented ranging from the 40s to the 90s. This broad age range shows that while CBD is primarily a disease of older adults, it can also affect individuals in the prime of their lives, leading to significant personal, social, and financial impacts.
Causes of CBD
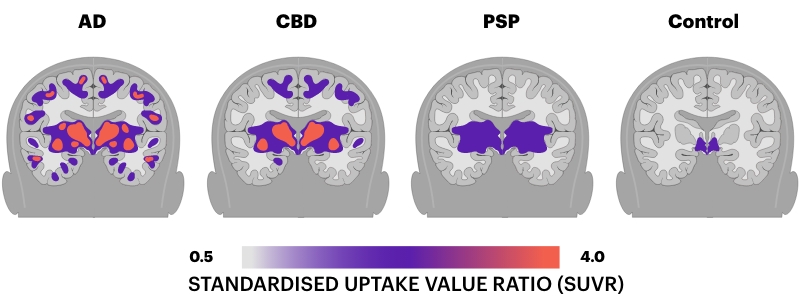
The primary cause of Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD) is the abnormal accumulation of tau protein within the brain’s neurons. This protein accumulation is similar to other tauopathies, such as Alzheimer’s disease, but has distinct features and progression patterns in CBD. The tau proteins in people living with CBD tend to clump together. Different to the tau clumping in people living with PSP, in CBD, tau clumps in a plaque-type way, which then leads to cell dysfunction and death, particularly in the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia. These areas are critical for coordinating movement and cognitive functions, explaining the typical CBD symptoms such as rigidity, impaired movement, cognitive decline, and speech difficulties.
The condition is characterised by symptoms affecting one side of the body, such as a limb becoming stiff, clumsy, or weak. Over time, symptoms often spread across the whole body and can significantly impair mobility and daily functioning. Distinctive symptoms of Corticobasal Degeneration include an “alien limb”, where an individual’s limb may move involuntarily, causing significant difficulties with activities of daily living such as dressing, feeding, and mobility.
The exact cause of tau clumping in CBD is still being studied. Genetic factors may play a role, although most CBD cases appear sporadically and rarely run in families. Environmental factors and other yet-to-be-identified triggers are also thought to contribute to the development of the disease.
WHY IS CBD DIFFICULT TO DIAGNOSE?
The diagnosis of CBD is complicated because its symptoms can closely resemble those of other neurological conditions. For example, the motor symptoms of CBD, such as stiffness and tremors, may be mistaken for Parkinson’s Disease, while its cognitive impairments might suggest Alzheimer’s Disease or Frontotemporal Dementia. Additionally, the rare and variable nature of CBD means that it may not be the first condition considered by healthcare professionals, further complicating the diagnostic process.
It is also important to mention that Corticobasal Syndrome (CBS) can result from different underlying neurological pathologies, including CBD, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Dementia, Stroke, and Multiple System Atrophy (MSA), and can present differently in all individuals. Hence, the progression of the disease may differ from one person to another, making diagnosis more challenging. The wide range of symptoms that can develop means that currently, there is no single test that can definitively diagnose CBD. Instead, the diagnosis is often made through a combination of clinical evaluation, neuroimaging, and the exclusion of other conditions. A definite diagnosis of CBD can only be made post-mortem.
The diagnosis of CBD relies on a careful assessment by specialists who are familiar with the range of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurologists typically use a combination of patient history, neurological examinations, and advanced imaging techniques such as MRI or PET scans to help distinguish CBD from other conditions. In some cases, genetic testing may also help to rule out hereditary factors associated with similar symptoms.
Watch The Video To Learn About Bruce And Neda’s Experience With CBD
SYMPTOMS OF CORTICOBASAL DEGENERATION (CBD)
CBD is a complex and progressive neurological disorder characterised by a variety of symptoms that significantly affect movement, cognitive functions, and daily activities. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management of the condition.
Below, we detail the different types of symptoms that can develop in CBD and how they can affect an individual.
Motor Symptoms
One-sided Presentation
One of CBD’s distinctive features is one side of the body is usually more affected than the other, particularly in the early stages of the disease.
Apraxia
This symptom involves difficulty with motor planning, leading to problems executing movements. People often show clumsy, awkward hand movements, which indicate a struggle to perform tasks that require fine motor skills.
Dystonia
This refers to abnormal postures of the hand, foot, arm, or leg due to muscle contractions. Dystonia in CBD contributes to the difficulty people face in maintaining normal postural alignment.
Involuntary muscle jerks
People may experience quick, involuntary muscle jerks, which are not only startling but also interfere with usual movements and can be distressing to the individual.
An “Alien Limb”
This unusual symptom involves the limb acting seemingly on its own, with the individual feeling as though it is not under their control. This can manifest as involuntary reaching or grasping.
Speech and Language Symptoms
Speech Difficulties
Speech in individuals with CBD may become slurred, distorted, or halting. Some people may exhibit stuttering, making communication increasingly challenging as the condition progresses.
Cognitive and Behavioural Changes
Cognitive Decline
Changes in personality, such as increased irritability, apathy, and low mood, are common. These symptoms reflect the broader cognitive impact of CBD, which can include impaired executive functions and decision-making abilities.
Late-Stage Symptoms
Swallowing Difficulties
Problems with swallowing typically occur in the later stages of CBD. Swallowing problems can lead to significant health complications, including an increased risk of aspiration and pneumonia.
Increased symptoms
Spread of symptoms such as apraxia and dystonia to both sides of the body.

LEARN MORE ABOUT COGNITION
AND BEHAVIOUR
Download our PDF to learn more about cognitive changes sometimes seen in PSP & CBD.
UNDERSTANDING THE IMPACT OF CBD
Living with Corticobasal Degeneration presents a range of challenges that can profoundly affect daily activities and independence. This progressive neurological disorder impacts various aspects of physical and cognitive functioning, leading to significant lifestyle changes and dependence on others. This section provides insights into how CBD affects daily life, accompanied by personal testimonials from individuals navigating these challenges.
The average CBD life expectancy typically ranges from 5 to 10 years after diagnosis, but it can vary widely depending on individual health factors and the quality of care. The progressive nature of CBD often leads to severe disability, requiring multidisciplinary care and support to improve the quality of life for those affected.
Impact on Daily Activities
CBD’s diverse symptoms, such as motor dysfunctions, cognitive decline, and speech difficulties, progressively impair an individual’s ability to perform day-to-day. Therefore, living with CBD may need individuals to adapt their way of life. Here are a few tips to help:
Home Adaptations
Adjusting your living environment can help to improve accessibility and safety for someone living with CBD. This may include installing grab bars, using non-slip mats, and organising the home to minimise the need for reaching or bending.
Equipment
Tools like text-to-speech devices, software that simplifies computer and smartphone use, and voice banking can help a person maintain independence in communication. Similarly, mobility aids can assist in navigation and reduce the risk of falls.
Professional Support
Engaging with physiotherapists, occupational, and speech therapists can provide the support needed to maintain independence for as long as possible. They offer exercises and techniques tailored to individual needs and progression of symptoms.
Community and Emotional Support
PSPA Support Groups, available either in person or online, can connect individuals and caregivers with others who understand their experiences. The groups provide a space for sharing experiences and tips as well as reducing feelings of isolation.
Navigating daily life with CBD is challenging, but adapting to the living environment, utilising assistive technologies, and community resources can significantly enhance the quality of life.
LISTEN TO THE EPISODE
Series 2 Episode 1 – Gilda shares her experience of living with CBD
SYMPTOM MANAGEMENT AND CARE FOR CBD
While there is currently no cure for CBD, there are ways to help alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for people affected. You may be offered support from multidisciplinary care teams and support networks like PSPA.
Available Therapies to Help Manage Symptoms:
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapists can design specific exercises that help maintain muscle strength and flexibility, which can prolong independence in daily activities and prevent falls.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapists work with people living with CBD to help them maintain their skills for daily activities. They also suggest home modifications and adaptive tools that make daily tasks easier and safer, such as modified utensils for eating, grab bars in bathrooms and customised seating.
Speech and Language Therapy
As speech and swallowing difficulties are common in CBD, speech and language therapists can provide advice to help people with their communication and adopt safe swallowing techniques.
Palliative Care
As CBD progresses, palliative care becomes essential for relieving symptoms and improving quality of life. This care includes pain management, nutritional support, and addressing psychological and spiritual needs.
PSPA plays a pivotal role in supporting individuals and families living with CBD by providing information and support services and advocating for better care and research into the disease. By developing informative publications and funding Corticobasal Degeneration research, PSPA aims to raise awareness of CBD, enhance the understanding of how it can impact daily life, and improve the standards of care for patients throughout the UK.
LIVING WITH CORTICOBASAL DEGENERATION
Download our PDF to learn more about what to expect from your care.
GENERAL BENEFITS AND ENTITLEMENTS FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH CBD
People diagnosed with CBD may find managing finances as challenging as dealing with the disease’s physical symptoms. However, various benefits and entitlements are available to help. This section outlines essential financial support and how to access it, ensuring that people living with CBD and their families are well-informed about their entitlements.
Disability-Related Financial Support
Attendance Allowance
This is available for individuals aged 65 or over who require help with personal care or supervision. Attendance Allowance is not means-tested, so eligibility does not depend on income or savings but on the individual’s care needs. It is paid at two rates, depending on the level of care required, and could also increase the amount of means-tested benefits you receive.
Personal Independence Payment (PIP)
For people under the age of 65, PIP can help with some of the extra costs associated with long-term ill health or disability. PIP consists of two components: daily living and mobility, which are assessed and paid at either a standard or enhanced rate depending on the individual’s circumstances. Like Attendance Allowance, PIP is not means-tested.
Disability Living Allowance (DLA)
Those who had already received DLA before it was replaced by PIP in 2013 continue to do so unless reassessed under the new system. DLA is for individuals who require help with mobility or personal care.
Adult Disability Payment (Scotland)
Adult Disability Payment is extra money to help you if you have a disability or long-term health condition that affects your everyday life. It has two parts: Daily Living and Mobility. You may qualify for one or both parts. The amount you get depends on how your condition affects your ability to do everyday activities and get around. Available to people in Scotland.
Support for Carers
Carer’s Allowance
If you care for someone with CBD for at least 35 hours a week, and they receive a qualifying disability benefit like PIP, Attendance Allowance, or DLA, you might be eligible for Carer’s Allowance. This benefit is available regardless of whether you live with the person you care for, but your earnings must not exceed a certain threshold.
Carer’s Credit
For those providing care for at least 20 hours a week but do not qualify for Carer’s Allowance, Carer’s Credit helps fill gaps in your National Insurance record, protecting your entitlement to the State Pension.
How to Claim
Applying for Attendance Allowance, PIP, and DLA: These benefits require the completion of specific forms available through the Department for Work and Pensions (DWP).
For Carer’s Allowance and Carer’s Credit: Claims can be made online or through telephone services provided by the DWP.
Additional Support
People living with CBD may also be eligible for other means-tested benefits depending on their circumstances, such as:
These benefits consider the individual’s income, savings, and other personal circumstances to provide additional financial support.

LEARN MORE ABOUT YOUR BENEFITS AND ENTITLEMENTS
This information sheet aims to provide you with an overview of the various benefits and entitlements available and how and where to apply for them.

PSPA Support and Information
PSPA offers support in navigating these entitlements, providing information and guidance on how to apply. The PSPA Helpline is a crucial resource for individuals and families, offering personalised support and information on accessing these benefits. You can contact the Helpline via the details below:
Telephone: 0300 0110 122
Email: helpline@pspassociation.org.uk
Understanding and accessing the available benefits can significantly relieve the financial pressures on individuals and families affected by CBD, allowing them to focus more on managing health and well-being.
RESEARCH AND HOPE FOR THE FUTURE
As the medical community continues to tackle CBD’s challenges, research plays a pivotal role in uncovering the mysteries of this complex condition. CBD research is focused on understanding its pathophysiology, improving diagnostic accuracy, and developing effective treatments. Studies primarily investigate the abnormal accumulation of tau protein in brain cells, which is believed to be a critical factor in the development of the disease. Researchers are exploring genetic factors that may predispose individuals to CBD, as well as environmental influences that could trigger its onset.
Advancements in neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI and PET scans, are being studied to improve the early detection of CBD. These tools help in differentiating Corticobasal Degeneration from other neurodegenerative diseases with similar symptoms.
In terms of treatment, clinical trials are testing various pharmacological treatments that aim to manage symptoms or slow the progression of the disease. This includes trials of medications that may reduce tau pathology or protect nerve cells from damage. Big leaps are being made in the field of Alzheimer’s research, which will hopefully aid in the advancement of PSP & CBD clinical trials.
Interested in being a participant in a research study or would you like to be involved with PSPA research activities? Register your interest here.
CBD PROFESSIONAL GUIDE
If you are receiving treatment or acting as a carer, download this guide to give to your healthcare professional to aid them in understanding and delivering treatment.
How can PSPA help?
PSPA is actively involved in progressing research into PSP & CBD by funding studies and collaborating with research institutions. We also facilitate networking among researchers and healthcare professionals to encourage collaborations that can lead to breakthroughs in the field.
Currently, PSPA is the only UK charity dedicated to creating a better future for everyone affected by PSP & CBD. In 2023, we introduced a new charity strategy to help focus our efforts in the future.
Our goals from the strategy are to:
- Enable people living with PSP & CBD and their families to live their best lives possible with high-quality support and information.
- Improve the quality of life of people living with PSP & CBD through research, education and awareness-raising.
- Put the voice of people living with PSP & CBD at the heart of what we do.
Watch the video below to hear our CEO talk about our strategy.
Overall, we aim to create a better future for everyone affected by PSP & CBD. We strive to improve diagnosis and discover treatment and, ultimately, a cure.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What are the early signs and symptoms of Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD)?
Early symptoms of CBD often start on one side of the body and may include stiffness, awkward limb movements, tremors, or trouble with coordination. Some people also experience changes in speech, memory, or mood. Many of these symptoms overlap with Parkinson’s and other neurological conditions, making early diagnosis more challenging.
Is Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD) linked to Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s Disease?
Although the motor symptoms of CBD, such as stiffness and tremors, may be mistaken for Parkinson’s Disease, while its cognitive impairments might suggest Alzheimer’s Disease or Frontotemporal Dementia, CBD is a distinctive condition that affects a different region of the brain and progresses differently. They are also caused by different factors. – For example, Parkinson’s is caused by the loss of dopamine-producing nerve cells in the brain, while Alzheimer’s is a tauopathy that affects different parts of the brain.
How is Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD) diagnosed?
There is no single test to definitively diagnose CBD. Diagnosis is often made through a combination of clinical evaluation, neuroimaging, and the exclusion of other conditions. A definite diagnosis of CBD can only be made post-mortem.
Is there currently a cure or treatment for Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD)?
Although there is currently no cure for CBD, there are ways to help alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life. Multidisciplinary care teams and support networks like PSPA can offer a range of support and care services, including opportunities to be part of research focused on slowing disease progression and finding effective treatment options.
What is the difference between Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD) and Corticobasal Syndrome (CBS)?
CBD is an underlying neuropathological disease that is defined by the accumulation of abnormal tau protein in the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia regions of the brain. It is commonly only confirmed by an autopsy of the brain post-mortem. CBS refers to a clinical diagnosis that is characterised by specific neurological symptoms such as apraxia, rigidity, dystonia, and speech and cognitive decline. CBS also has other neurological causes, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, among others.
What is the average life expectancy of people living with Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD)?
The life expectancy of people with CBD varies from person to person. In the case of CBS, the underlying cause determines the life expectancy. On average, people live between six and eight years after first developing symptoms.
What kind of support is available for people with Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD), their carers, and family members?
As the only UK charity for CBD, PSPA offers a range of support services to people living with the condition, their carers, and family members. These include a dedicated PSPA Helpline service, regional and online Support Groups, Link Volunteer service, PSPA Support Grants, and various information resources. You may also get professional support from physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and speech therapists, as well as external resources like Adult Social Care, local carer organisations, and specialist palliative care services, among others.


